Glossary – Red Snapper Specific
- Abundance: Numbers of red snapper individuals in the Gulf of Mexico (GoM) stock.
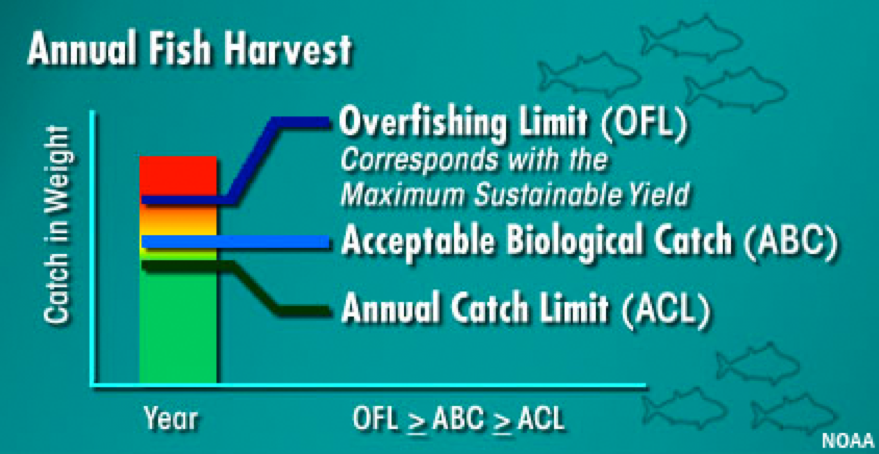
- Acceptable Biological Catch (ABC): The annual red snapper catch level recommended for the GoM stock by the Gulf of Mexico Fisheries Council’s Scientific and Statistical Committee (SSC).
- Accountability Measures (AMs): Regulations that try to keep the total red snapper catch within the GoM under the annual catch limit (ACL).
- Accuracy: A measure of how close an estimated parameter (e.g., in the GoM red snapper stock assessment) is to the true value. Compare precision.
- Allocation: The share received by a sector or a component (e.g., for the GoM red snapper fishery, there are the Commercial Sector, the Recreational Sector, within the Recreational Sector, there are the Federal For-hire Component and Private Angling Component). Sometimes the allocation is based on the historic harvest amounts.
- Annual Catch Limit (ACL): The amount of red snapper that can be caught by fishermen in GoM over one year.
- Assessment error: Uncertainty resulted from imperfect GoM red snapper stock assessment.
- Annual Catch Target (ACT): Annual harvest goal for the GoM red snapper fishery.
- Bag limit: A law imposed on fishermen restricting the number of red snappers they may kill and keep.
- Beverton-Holt Model: A classic discrete-time stock-recruitment model, which assumes the a globally asymptotically stable equilibrium for the red snapper recruitment.
- Bias: A consistent under- or over-estimate of the true population parameters (e.g., in the GoM red snapper stock assessment).
- Biological reference point: Benchmarks of GoM red snapper stock status from a biological perspective.
- Biomass: The aggregate weight of the GoM red snapper stock.
- Bycatch: The red snapper individuals that are harvested in the GoM shrimp fisheries, but not sold or kept. It does not include the individuals released alive.
- Coefficient of variation (CV): A measure of relative variability for parameters (e.g., in the GoM red snapper stock assessment). It is the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean (average).
- Discards: The portion of the red snapper catch, which is not retained on board.
- Fecundity: The reproductive capacity of a red snapper individual, usually measured as the number of eggs produced by a female in one spawning event.
- Fisheries regulations: Controls designed to restrict either effective fishing effort (input controls) or the total catch (output controls) to predefined limits in the GoM red snapper fishery.
- Fishing mortality: A measurement of the rate of removal of red snapper from the GoM stock by fishing.
- Harvest control rule (HCR): The pre-agreed guidelines for how many red snappers can be caught based on how well (or poorly) the GoM stock is doing.
- Implementation error: The difference between a management goal for the GoM red snapper and the actual realized fishing mortality rate.
- Individual Fishing Quota (IFQ): The red snapper IFQ program is a single-species, single-share category program, that started in the year of 2007. This program allocates quota to a shareholder, who then has a guaranteed share (which may be either harvested or traded) of the Total Allowable Catch (TAC).
- Kobe plot: A common visualization method in management strategy evaluation to represent the annual trajectory of the GoM red snapper fishery over time and examine the proportion of time that the fishery stock spends in different status. The Kobe plot is divided into four panels. The red panel (upper left) corresponds to the “overfished and overfishing phase”. The green panel (lower right) is the “no risk” area. The two yellow panels (overfishing and overfished) characterize intermediate situations.
- Management strategy evaluation (MSE): A simulation tool to quantify the risk of the GoM red snapper fisheries, and allow stakeholders to test alternative potential harvest strategies.
- Maximum sustainable (sustained) yield (MSY): The maximum harvest that the GoM red snapper fishery can be sustained without reducing population productivity year after year (long-term), or for the next a few years (short-term).
- Maximum Fishing Mortality Threshold (MFMT): The threshold above which the GoM red snapper stock is said to be experiencing overfishing.
- Minimum legal size: A regulation in which captured red snapper individuals smaller than a prescribed minimum size must be returned to the sea.
- Minimum Stock Size Threshold (MSST): The spawning stock biomass level at which the GoM red snapper stock is declared overfished, and a rebuilding plan must be implemented. Right now, it is 50% of BMSY.
- Natural mortality: A measurement of the rate of the removal of red snapper from the GoM stock due to causes associated with natural factors; such causes can include disease, competition, cannibalism, old age, predation, pollution and so on.
- Lognormal distribution: A continuous probability distribution of a random parameters whose logarithm is normally distributed. It is one of the most prevalently used distributions used in Fisheries Sciences.
- Observation error: Uncertainty assuming that the state of the GoM red snapper fishery system cannot be observed perfectly.
- Overfished: A status of a stock “whose size is sufficiently small that a change in management practices is required in order to achieve an appropriate level and rate of rebuilding.” For example, according to the 2016 stock assessment, the GoM red snapper was not overfished.
- Overfishing: A rate or level of fishing mortality that jeopardizes the capacity of a fishery to produce the maximum sustainable yield on a continuing basis. For example, according to the 2016 stock assessment, the GoM red snapper was not overfishing.
- Overfishing limit (OFL): The catch level of the GoM red snapper stock, above which overfishing is occurring. It is calculated as the median (50th percentile) of the probability density function of retained yield using the projection of FSPR26% (i.e., the yields that achieved the SSB target in equilibrium).
- Percentile: A measure used in statistics indicating the value, below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations falls.
- Performance measure: Statistics in the projection of the GoM red snapper fishery to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of management strategies.
- Precision: A measure of repeatability, or of how close repeated measurements are to one another. Compare accuracy.
- Process error: Additional variability in the GoM red snapper fishery that is not represented by the main structure of the stock assessment model.
- Quota: A limit on the weight of the red snapper that may be caught in the GoM.
- Randomization: Assuring that each individual in the GoM red snapper stock has some probability of selection.
- Random seed: A starting point in generating random numbers.
- Recruitment: The number of red snappers surviving to enter the GoM fishery.
- Release mortality: The death of the red snapper individuals that caught alive and then die after release.
- Retention: The amount of red snapper individuals that fishermen can catch and keep.
- Risk assessment: The assessment of risks associated with a particular (management) strategy; e.g., the probability that the size of the GoM red snapper stock will drop below a defined reference point.
- Robustness: A measure that the GoM red snapper fishery can remain unaffected by changes in the test management strategies.
- Sample size: The number of items or measurements in a sample.
- Selectivity: The ability of a gear to catch a certain size of red snapper relative to its ability to catch other sizes.
- Stock assessment: Process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting demographic information to determine changes in the abundance of the GoM red snapper fishery stock in response to fishing and, to the extent possible, predict future trends of stock abundance.
- Stock mixing: Individuals in one GoM red snapper sub-stock (e.g., the East Gulf) come from the other (the West Gulf).
- Stock spawning biomass: The total weight of the GoM red snapper stock that is old enough to spawn.
- Stock Synthesis: An age-structured population dynamics model that is used to assess the impact of fisheries on fish and shellfish stocks while taking into account the influence of environmental factors. For example, the GoM red snapper stock assessment was conducted under Stock Synthesis 3.
- Total allowable catch (TAC): The maximum catch allowed from the GoM red snapper fishery in accordance with a specified management plan.